The Future of Aging: Healthtech Innovations Reshaping Elderly Care & Well-being

The global population is aging, and the physical and emotional challenges elderly individuals face are undeniably complex. But what if technology could provide the solutions they have been waiting for? Many seniors find themselves struggling not only with health conditions but also with a lack of accessible, personalized care.
Healthtech innovations are stepping in to address these challenges, offering more than just convenience; they are reshaping the entire landscape of elderly care. Imagine a world where seniors can live more independently, stay connected to healthcare providers from their homes, and monitor their health with a simple touch - this vision is increasingly becoming a reality.
This article explores how these groundbreaking technologies are enhancing the quality of life for the elderly and tackling long-standing issues within healthcare systems.
The Aging Population: A Global Shift
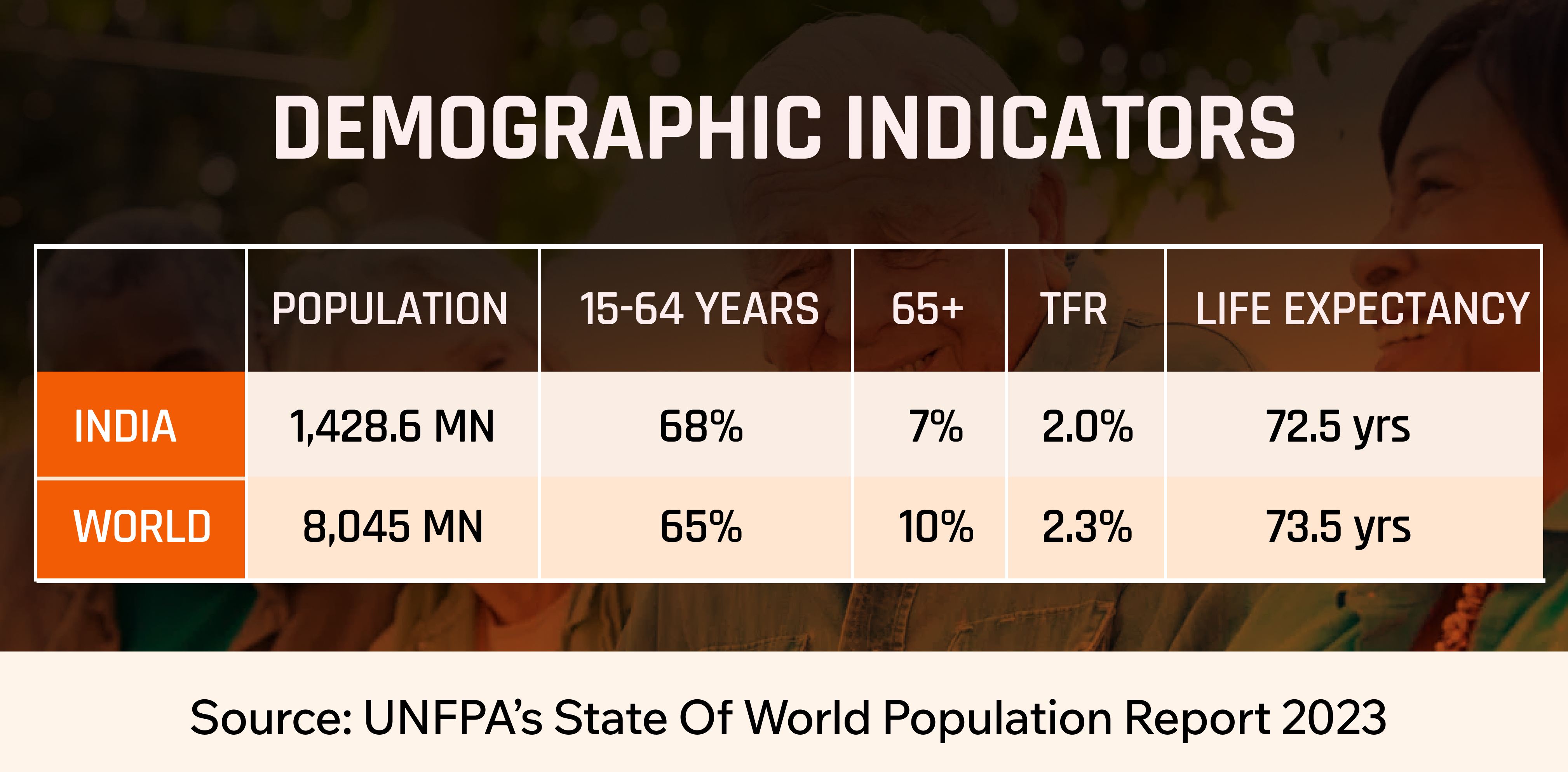
According to a 2024 report by the World Health Organization (WHO), the proportion of people aged 60 years and older is steadily rising, and this demographic is expected to double by 2050, reaching 2.1 billion. In India alone, the elderly population is projected to surpass 300 million by 2050. According to the India Ageing Report (2023) by UNFPA, India has witnessed moderate to high decadal growth in the elderly population since 1961. The pace was slower before 2001 but is expected to increase sharply in the coming decades.

Additionally, the increase in life expectancy brings about various challenges in elderly care, such as accessibility to healthcare, managing chronic conditions, financial strain, and the risk of isolation.
This demographic shift presents an urgency to rethink how we care for our aging population, and technology has emerged as a powerful catalyst for change. Healthtech innovations are not just enhancing elderly care but empowering individuals to have an improved quality of life with dignity.
Key Challenges
Before exploring healthtech solutions, it is essential to understand the challenges that hinder elderly care today.
Access to Healthcare: As seniors age, they often face mobility issues, making it challenging to visit healthcare facilities. For those in rural areas or developing countries, healthcare services may be far and few, exacerbating the problem. According to a report titled 'State of Healthcare in Rural India-2023,’ more than 60% of people from rural areas chose to "migrate" out of their state to avail themselves of treatment for major diseases.
Chronic Conditions: Many elderly individuals suffer from multiple chronic conditions, such as diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease. Managing these conditions requires constant monitoring, which can be both cumbersome and expensive. According to a CDC study (2020), 51.8% of US adults had at least one chronic condition, and 27.2% had multiple chronic conditions in 2018. Prevalence was highest among women, non-Hispanic white adults, adults aged 65 or older, and those living in rural areas.
Caregiver Support: In most cases, elderly individuals rely on family members or professional caregivers for support. However, there is often a shortage of qualified caregivers, and those who do exist may not have the necessary resources or training to manage the needs of older adults.
The old-age dependency ratio of a population represents the number of persons aged 60+ years per 100 persons in the 15–59 years (or working-age) group. The higher the ratio, the greater the old age-related dependency, reflecting higher levels of demand for care from immediate family. As per the India Ageing Report (2023) by UNFPA, population projections indicate that in 2021, there were 16 older persons per 100 working-age persons in India, with significant variations across regions.
Hence, the lack of caregiver support for elderly individuals living alone is a growing concern and leaves many seniors vulnerable to health risks, isolation, and unmet daily needs.
Financial Burden: Elderly care places a significant economic burden on individuals and families, especially in countries without comprehensive healthcare systems. Healthcare costs, including doctor visits, medications, and assisted living, are often unaffordable. As per data collected during the 75th round of the National Sample Survey (NSS), older adults spend about 17.4% of household consumption expenditures on healthcare services. The poorest older adults spend the highest share of consumption expenditures (24.8%) on healthcare among economic quantiles. Further, it was revealed that about 81% of older adults do not have any type of health insurance coverage in India.
Social and Psychological Issues: Loneliness and isolation are common among older adults, particularly those living alone or with limited family support. Mental health issues, such as depression and anxiety, are prevalent in this population, and many lack access to social interaction or mental health care.
Healthtech Solutions Benefiting Elderly Care
Health technology is transforming elderly care in unprecedented ways. From wearable devices to AI-powered tools, innovations are making it easier for elderly individuals to manage their health, maintain independence, and stay connected to loved ones and healthcare professionals.
Some noted breakthroughs in the healthtech sector include:
Remote Patient Monitoring: One of the most significant advancements is wearable devices that continuously monitor vital signs such as heart rate, glucose levels, and blood pressure. Wearable health monitors, such as Apple Watch and Fitbit, track physical health and send real-time alerts to caregivers and healthcare providers in case of anomalies. Further, it allows for prompt intervention, preventing emergencies and reducing hospital readmissions.
Evinova, a global leader in clinical trial technology, recently partnered with Quantum Leap Healthcare Collaborative (QLHC) to incorporate its remote patient monitoring (RPM) solution into the ongoing I-SPY 2.2 clinical trial. I-SPY 2.2 is the largest and longest-running platform trial that evaluates multiple innovative therapeutic treatments for women with newly diagnosed, locally advanced breast cancer.
Therefore, for seniors who often face mobility challenges and chronic health conditions, RPM offers the comfort of being cared for from the safety of their homes. These tools go beyond data—they preserve dignity and independence while enabling older adults to live healthier lives.
Telemedicine: Telemedicine is transforming elderly care by addressing critical challenges and improving healthcare accessibility. It enables virtual consultations, eliminates the need for travel, and provides convenience for seniors with mobility issues or those in remote locations. Additionally, telemedicine fosters continuity of care through seamless communication between seniors and healthcare providers, promoting better coordination and consistent treatment. As a transformative healthtech solution, telemedicine enhances the quality of life and healthcare outcomes for older people.
Assistive Technologies: The World Health Organization (WHO) defines assistive technologies as -
“Assistive technology is an umbrella term for assistive products and their related systems and services. Assistive products help maintain or improve an individual’s functioning related to cognition, communication, hearing, mobility, self-care, and vision, thus enabling their health, well-being, inclusion, and participation.”
Various assistive technologies are helping older adults maintain their independence and safety. These include AI-powered devices such as smart wheelchairs, smart walkers, exoskeletons, and AI-powered fall detection systems, all of which support elderly autonomy and well-being.
Recently, US-based CarePredict launched CarePoint, a groundbreaking real-time care charting system designed to revolutionize senior living care delivery. Devices such as the CarePredict system have been shown to reduce falls by 69% as they use sensors to monitor the daily activity of elderly individuals, providing caregivers with valuable insights and alerting them to any fall or medical emergency.
Medication Management: Medication adherence is crucial in managing chronic conditions, yet many seniors struggle to remember complicated medication schedules. Smart pill dispensers and medication management apps, like Medisafe, aid seniors stay on track with their prescriptions by sending reminders and automating pill dispensing. The company recently introduced PATHWAYS, a tool designed for Alzheimer's Disease (AD) treatment. It supports healthcare providers in managing AD patients by efficiently tracking dosing schedules and monitoring protocols for FDA-approved monoclonal antibodies indicated for AD.
AI and Predictive Analytics: Artificial intelligence is pivotal in early diagnosis and predictive analytics for elderly care. AI tools can analyze wearable devices, medical records, and imaging data to identify potential health risks before they manifest.
For instance, AI algorithms are being used to detect early signs of Alzheimer's disease, heart disease, and stroke, enabling timely intervention and treatment. Researchers at the University of Missouri have developed a portable system to detect early cognitive decline. Reportedly, this low-cost portable device identifies motor function changes associated with cognitive decline. These AI-powered motor function assessments provide an affordable and effective method for the early detection of mild cognitive impairment (MCI), a condition often seen as a precursor to dementia.
Recently, Google has entered the healthcare industry to revolutionize it through advanced diagnostics, personalized medicine, and preventative care. Google Assistant is being integrated into healthcare by allowing patients to ask medical questions, book appointments, or check symptoms via voice commands, thereby enhancing accessibility to healthcare services.
Additionally, a new Google feature called ‘What People Suggest’ will aggregate relevant online discussions and expert insights into easy-to-understand themes. For example, users searching for arthritis-friendly exercises will receive suggestions based on real-life discussions.
Virtual Reality (VR): VR applications are used for various purposes, from physical therapy to combating social isolation. VR-based cognitive training programs are helping seniors maintain mental acuity, while virtual social platforms allow them to connect with friends and family in immersive environments.

India’s Shift Towards Tech-Driven Elderly Care
The Indian government launched the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) in 2021 to cater to the growing population of older adults and promote tech-driven care for the elderly. ABDM facilitates an integrated digital health infrastructure supporting universal health access. The mission prioritizes the security and privacy of personal health information and aims to bridge the digital divide across the country.
Last year, Yashoda Super Speciality Hospital in Uttar Pradesh unveiled its 'SmartCare Monitoring' program in collaboration with Dozee. The initiative integrated remote patient monitoring (RPM) and an early warning system (EWS) across all ward beds. It allows personnel to track vital signs remotely, including heart rate, respiration rate, blood pressure, SPO2 levels, temperature, and ECG.
Telehealth services have also gained considerable traction, especially in remote or underserved regions. For seniors who struggle with mobility or live in rural areas, telemedicine offers a convenient way to consult with doctors without needing to travel. For example, e-Sanjeevani, India's national telemedicine service, has significantly expanded its reach since its inception. As of December 2022, the platform has facilitated over 80 million teleconsultations. By June 2024, this number had surged to 276 million consultations, highlighting its rapid adoption and impact.
Economic & Social Impact
Healthtech innovations have improved the quality of care and made elderly care more economically sustainable.
Reduced Hospital Admissions: With remote monitoring and telehealth services, elderly individuals can manage their health more effectively at home, leading to fewer hospital visits. This reduces the overall strain on healthcare systems and alleviates the financial burden on families.
Lower Healthcare Costs: Remote monitoring and virtual consultations are far more cost-effective than in-person visits, especially for individuals who live in remote areas or require regular check-ups. Telemedicine has been shown to reduce healthcare costs by cutting transportation expenses and the need for in-person visits.
Alleviation of Caregiver Stress: Caregivers, who are often family members, face immense physical, emotional, and financial stress. Healthtech tools, such as fall-detection systems and remote patient monitoring, provide them with the support they need to offer high-quality care without the constant worry of an emergency occurring.
Roadblocks
Despite the numerous benefits, there are still challenges in implementing health tech solutions for elderly care.
Access to Technology: In many developing regions or rural areas, access to technology remains limited. This digital divide means many seniors may not benefit from health tech innovations. Ensuring healthtech solutions are affordable and available to all demographics will be crucial for future success.
The WHO and UNICEF Global Report on Assistive Technology (2022) demonstrated considerable inequity in access to assistive technology. As few as 3% of people in some low-income countries were reported to have access to the assistive products they need, compared to 90% in some high-income countries.
Data Privacy and Cybersecurity: With the rise of digital health technologies comes the risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks. Protecting sensitive health data is paramount, and more robust cybersecurity measures need to be developed to gain the trust of elderly users and their families.
Digital Literacy: Many seniors face difficulties using new technologies due to lacking digital literacy. For healthtech to be genuinely beneficial, educational initiatives and user-friendly interfaces must be prioritized to ensure that elderly individuals can use the technology effectively.
The Way Forward
In the future, the potential for healthtech in elderly care is vast. Integrating emerging technologies such as AI, the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain could revolutionize elderly care.
To ensure that healthtech benefits all seniors, regardless of socioeconomic status, governments, tech companies, and healthcare providers must unite to make these technologies more inclusive and affordable. To make this vision real, we need deeper collaboration between policymakers, innovators, and care providers—so that no senior is left behind.
Stay tuned for more such updates on Digital Health News
































